Bed bugs are among the most persistent and challenging pests to eliminate. Their ability to reproduce quickly contributes significantly to infestations. Understanding the bed bug reproductive process helps in their prevention and management.
In this article, we will explain how bed bugs reproduce, their reproduction rate, and how to stop them from multiplying.
 Visit our Species, Control, and DIY Guide sections for additional resources on bed bugs and ways to tackle a bed bug infestation.
Visit our Species, Control, and DIY Guide sections for additional resources on bed bugs and ways to tackle a bed bug infestation.


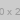
 Taking proactive measures can lower the chances of an infestation. If things seem to have gone out of control, get help from pest control experts. Our team can provide a customized approach to protect your home effectively.
Taking proactive measures can lower the chances of an infestation. If things seem to have gone out of control, get help from pest control experts. Our team can provide a customized approach to protect your home effectively.

What Are Bed Bugs?
Bed bugs are small, parasitic insects that feed on human blood. These pests are flat, oval, and reddish-brown in color, typically hiding in cracks and crevices. Known for their nocturnal feeding habits, bed bugs infest areas like mattresses, furniture, and baseboards. Their rapid reproduction is one of the reasons they are difficult to control.How Do Bed Bugs Reproduce?
Bed bugs have a fascinating and unique reproductive process, allowing their populations to grow rapidly under favorable conditions. Mating Process Bed bugs reproduce through a method called traumatic insemination. Male bed bugs pierce the female’s abdomen with a needle-like organ, injecting sperm directly into her body cavity. This unusual method allows females to store sperm and fertilize eggs over time. Egg Laying After mating, female bed bugs lay 1 to 5 eggs daily, accumulating to about 200 to 500 eggs over their lifetime. These tiny, pinhead-sized eggs are often hidden in cracks, crevices, and secluded areas close to feeding sites.Development Stages of Bed Bugs
-
Eggs Hatch: The eggs hatch into nymphs, which are smaller, pale versions of adult bed bugs.
-
Nymph Growth: Nymphs molt five times, requiring a blood meal at each stage to progress.
-
Adult Maturity: After their final molt, nymphs become fully developed adults, ready to mate and continue the cycle.


Not getting a solution?
Get your free pest control estimate today!How Fast Do Bed Bugs Reproduce?
Bed bugs reproduce and mature quickly, allowing infestations to escalate rapidly under ideal conditions. Their full life cycle, from egg to adult, typically takes 6 weeks to 2 months, influenced by factors such as temperature and access to food. Female bed bugs commonly lay 1 to 5 eggs daily, which means even a small initial population can grow into a significant infestation in a short period. Under ideal conditions, a bed bug infestation can grow rapidly. In just a few months, what starts as a small group of bed bugs can explode into a large infestation. How to Prevent a Bed Bug Infestation? Preventing bed bugs from reproducing is essential to managing infestations effectively. Follow these practical steps to reduce their spread and growth:Bed Bug Control Tips
-
Inspect regularly for bed bugs in mattresses, bed frames, and furniture cracks.
-
Use heat treatments on infested items to kill eggs, nymphs, and adults.
-
Encase mattresses to prevent bed bugs from hiding and reproducing.
-
Contact professional pest control services for comprehensive treatment targeting all life stages.
 Taking proactive measures can lower the chances of an infestation. If things seem to have gone out of control, get help from pest control experts. Our team can provide a customized approach to protect your home effectively.
Taking proactive measures can lower the chances of an infestation. If things seem to have gone out of control, get help from pest control experts. Our team can provide a customized approach to protect your home effectively.





